
A hard refresh offers a quick and easy way to clear the browser’s cache for a specific page, forcing it to load the latest and greatest version of it. If changes made to a web application or website don’t register immediately due to caching, a hard refresh will usually fix this, though occasionally completely clearing the cache may be necessary. Sometimes, the only way to see updates is by doing a hard refresh or by clearing the entire cache of the browser. While enhancing performance is usually a great thing, cached resources can cause problems when you have a major change to a web application’s JavaScript or style sheets, as we have with the redesigned charts in AdviserGo. Modern browsers like Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Firefox and Safari tend to cache front-end resources like JavaScript and style sheets (CSS) to increase web application and website performance. The following article details how to do a hard refresh in the most common browsers - Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Firefox and Safari - on both Windows and Mac.īrowser caching is useful for web browsing in that it allows for page that you’ve visited previously to load much more quickly. The cache remembers parts of pages, like images, to help them open faster during your next visit.Does AdviserGo look out of sorts following a recent update? A hard refresh may be needed.They make your online experience easier by saving browsing data. Cookies are files created by sites you visit.Some sites can seem slower because content, like images, needs to load again.If you turn sync on in Chrome, you’ll stay signed into the Google Account you’re syncing to in order to delete your data across all your devices.For example, if you were signed in, you’ll need to sign in again. If you use Safari, Firefox, or another browser, check its support site for instructions. For example, you can delete cookies for a specific site. Learn how to change more cookie settings in Chrome. Next to "Cookies and other site data" and "Cached images and files," check the boxes.
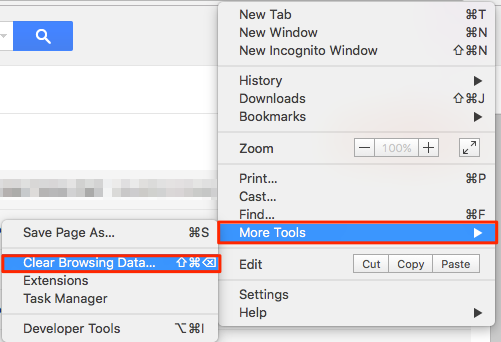
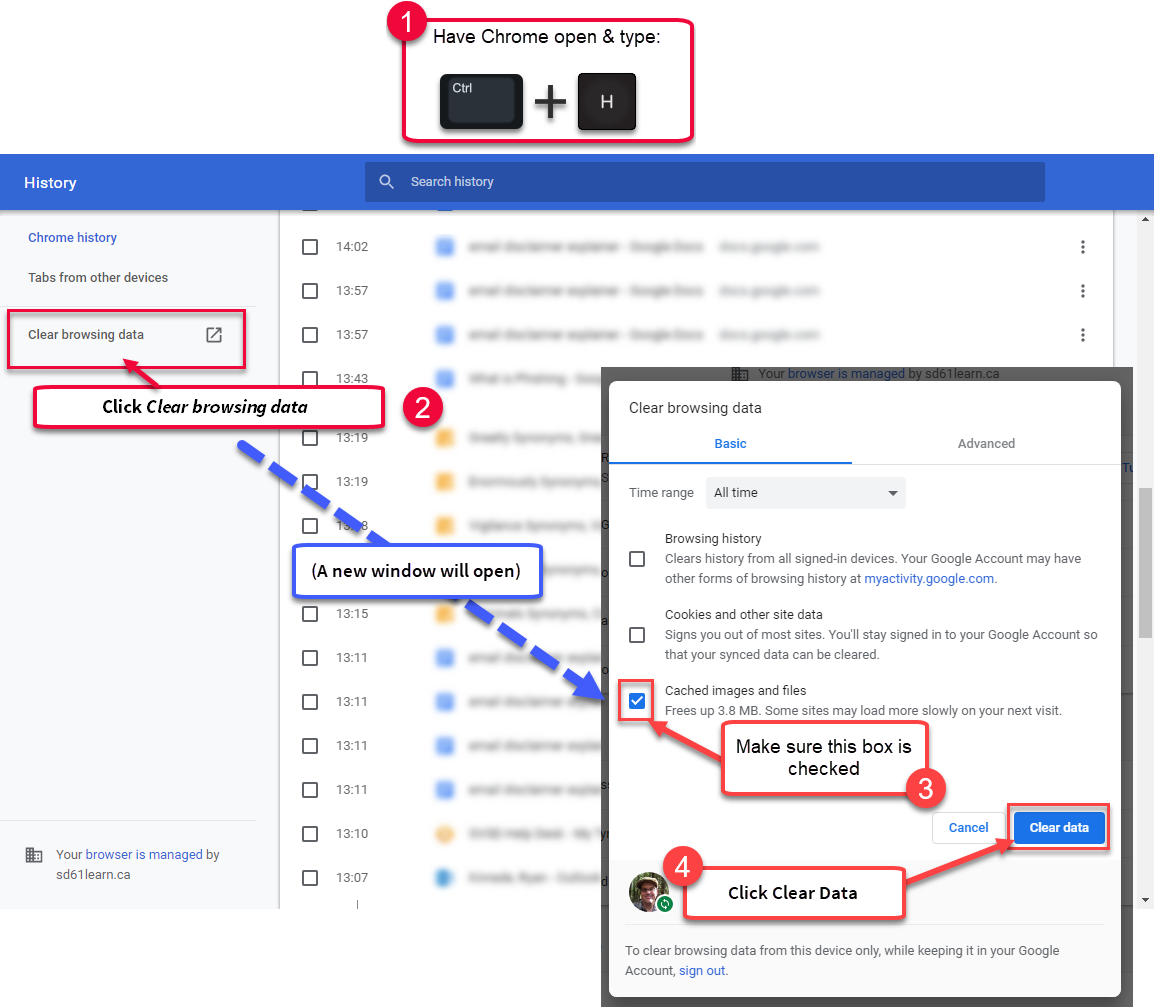
Clearing them fixes certain problems, like loading or formatting issues on sites. When you use a browser, like Chrome, it saves some information from websites in its cache and cookies.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
